Understanding how Google Search works is really important for anyone looking to use digital marketing effectively or simply curious about the workings behind the world's most popular search engine.
How Google Search works is a complex process that involves crawling and indexing web pages, analyzing user queries, and ranking search results based on relevancy algorithms.
Google Search operates on a complex algorithm designed to provide the most relevant and useful results to users' queries from billions of web pages.
Here's a breakdown of its core components and how they function together to deliver search results.
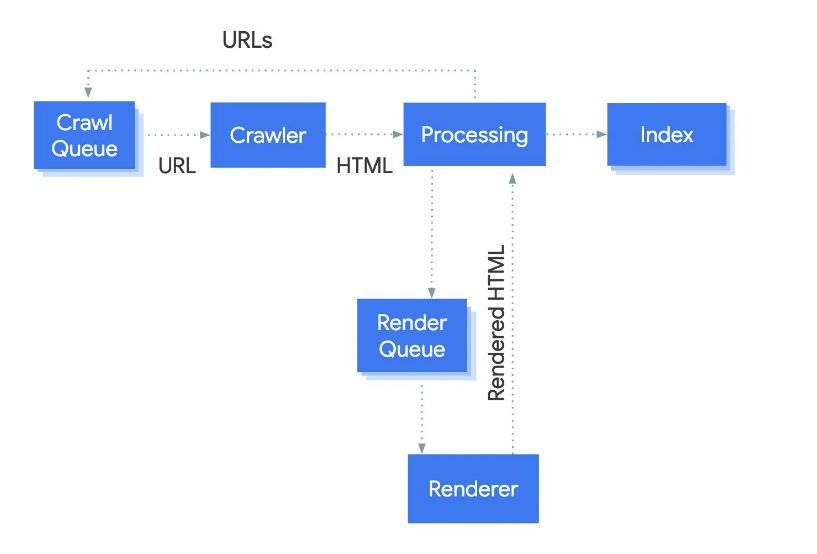
Crawling and Indexing
Crawling and indexing are foundational to the functioning of search engines, playing a critical role in digital marketing strategies. Understanding these concepts helps in optimizing websites to ensure they are visible and rank well on search engine results pages (SERPs). Let's dive into these processes, their significance in SEO, and provide examples to illustrate their impact.
Crawling: The Discovery Phase
Crawling is the first step in the search engine process, where search engine bots, often referred to as crawlers or spiders, visit web pages. These bots systematically browse the internet to discover new and updated content, which can be anything from webpages, images, videos, to PDF documents. The discovery of content is primarily dependent on links; crawlers follow links from one page to another and record the information they find. This process is initiated in several ways, including adding new websites directly through search engine tools or discovering links from existing pages.
Example of Crawling:
Consider a new blog post on digital marketing strategies that is published on a website. A search engine crawler finds this post because it follows a link from another page on the same website or from an external site linking to it. The crawler analyzes the content, including text, images, and any other media, to understand what the page is about.
Indexing: The Organizing Phase
After discovering content through crawling, search engines move on to the next step: indexing. Indexing involves analyzing and storing information found during crawling in a vast database known as the index. The index is like a giant library that search engines reference when processing search queries. Information is categorized and organized so that it can be quickly retrieved when needed. Not all content discovered during crawling is indexed; search engines use algorithms to decide which pages are of sufficient quality and relevance to be included in the index.
Example of indexing:
Following the earlier example, once the search engine crawler analyzes the new blog post on digital marketing strategies, it decides to add this content to its index based on its relevance, uniqueness, and value to searchers. The post is now eligible to be displayed as a result of relevant search queries.
Importance in SEO
The processes of crawling and indexing are crucial for SEO for several reasons:
- Visibility: For a webpage to appear in search results, it must first be crawled and indexed.
- Content Updates: Regularly updated content encourages frequent crawling, which can help maintain or improve SERP rankings.
- Website Structure: A well-organized website with clear navigation and internal linking facilitates easier crawling and indexing, positively impacting SEO.
Real-World Example: Google's Freshness Algorithm
Google's freshness algorithm update emphasizes the importance of recent content for certain types of search queries. Websites that regularly update their content are more likely to be crawled frequently, offering opportunities to secure or improve rankings for relevant queries.
Google discovers new and updated content, such as web pages, images, and videos, through a process known as crawling. It uses software called Googlebot to automatically visit websites across the Internet. Googlebot starts with a list of webpage URLs from past crawls and sitemaps provided by website owners. As it visits these URLs, it detects links on each page and adds them to its list of pages to crawl. New sites, changes to existing sites, and dead links are noted and used to update Google's search index.
2. Algorithms and Ranking
Google Search uses a series of algorithms to analyze and rank websites based on their relevance to the search query.
These algorithms determine how content is ranked on search engine results pages (SERPs). Google, for instance, uses a complex array of algorithms to assess over 200 factors that influence website rankings.
These factors include the relevance and quality of content, user engagement signals (like click-through rates and time spent on a page), the number of inbound links, and the overall user experience on a website. In order to provide the most accurate and trustworthy website rankings, search engines continuously evaluate and update these factors.
Key Google Ranking Algorithms
Google's ranking algorithms are particularly influential in digital marketing, given Google's dominance in the search engine market. Some of the key Google algorithms include:
- Hummingbird: Focuses on understanding the context and intent behind search queries to provide more accurate search results.
- Pigeon: Enhances local search results by prioritizing local information and improving the way Google handles and interprets location cues.
3. Search Queries and User Intent
When a user types a query into Google Search, the system interprets the search intent—whether the user seeks knowledge, specific websites, or local services. The relevance of webpages in relation to the query is assessed, considering factors like region, language, and device type. Google aims to deliver the most relevant results first, sometimes incorporating special features (e.g., maps, images, news) that enhance the search experience based on the perceived user intent.
4. Freshness and Content Quality
Content freshness and quality are crucial factors in the ranking process. Google tends to prioritise newer content for time-sensitive searches while maintaining older, authoritative content for queries where freshness is less critical. High-quality, original content that matches the search intent and provides comprehensive information on the topic tends to rank higher. This includes the strategic use of keywords, fulfilling user search intent, and providing a positive user experience.
5. User Experience and Page Usability
Google places a significant emphasis on user experience (UX), which encompasses page load speed, mobile friendliness, intuitive navigation, and the absence of intrusive ads or pop-ups. Ensuring a website meets these UX criteria can positively affect its visibility in search results. Google's Core Web Vitals are a set of specific factors that measure a page's health in terms of loading performance, interactivity, and visual stability.
6. Authority and Expertise
Establishing topical authority and expertise through comprehensive coverage of a subject area and acquiring backlinks from reputable sources within that niche can further enhance a site's ranking. Google aims to provide users with results from sources that demonstrate a deep understanding of and authority on the topic at hand.
7. Algorithm Updates
Google continuously updates its algorithms to improve the search experience, introducing major changes several times a year that can significantly impact website rankings. Staying informed about these updates and adjusting strategies accordingly is essential for maintaining and improving search visibility.
In essence, Google Search functions as a sophisticated gateway to the vast information available on the Internet, using a blend of technological processes and algorithms designed to connect users with the most relevant, authoritative, and useful content related to their queries.
For digital marketers and content creators, understanding and aligning with these processes—through SEO best practices, content quality, and user experience optimization—is key to achieving visibility and success in search results.


